Mako robotic-arm assisted hip and knee replacement surgery is cutting edge technology that provides each patient with a personalized surgical plan based on the unique anatomy of their hip or knee. It has been developed in the United States and has recently introduced to Australia. Dr Limbers is one of the first surgeons in Australia to use this technique.
Mako Robotic Partial Knee Replacement
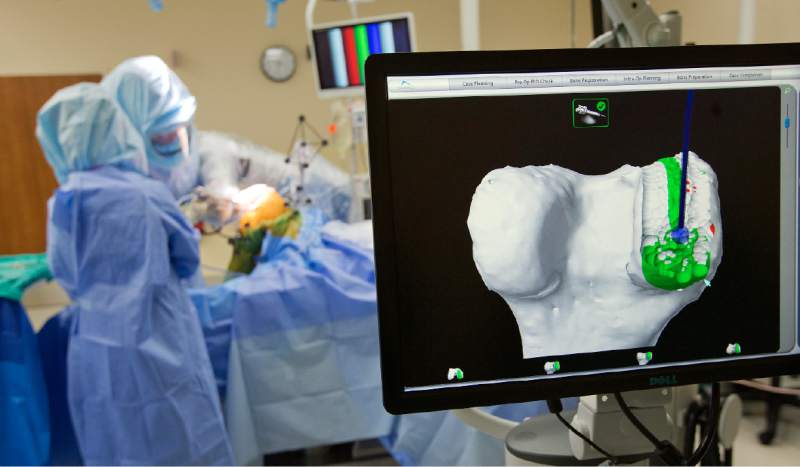
Mako robotic surgery can be used for partial (unicompartmental) knee replacement, which is a procedure designed to relieve pain caused by joint degeneration due to osteoarthritis in one compartment of the knee. By selectively targeting the part of your knee damaged by osteoarthritis, Dr Limbers replaces the diseased part of your knee while sparing the healthy bone and ligaments surrounding it. The Mako technology provides Dr Limbers with a patient specific 3-D model to pre-plan your partial knee replacement. During surgery, he guides the robotic-arm (Figure 1) based on your patient-specific plan. This allows him to remove only the diseased bone, preserving healthy bone and soft tissue, and assists him in positioning the implant based on your anatomy.
Prior to surgery a CT scan of your knee is performed and is used to generate a 3D virtual model of your knee. This virtual model is loaded into the Mako system software and is used to create your personalized pre-operative joint replacement plan.
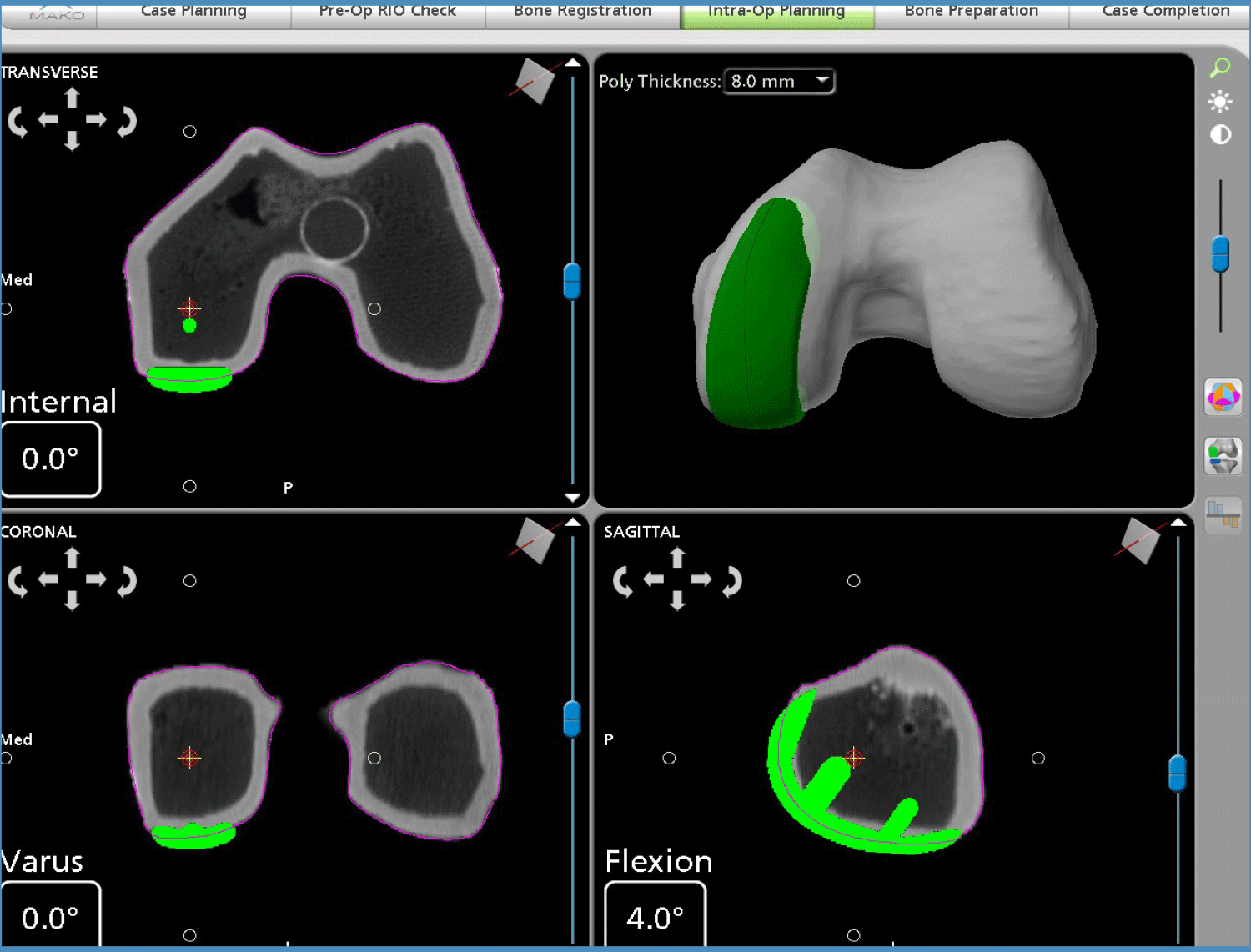
In the operating room, Dr Limbers performs a minimally invasive approach to your knee and inserts navigation pins into the femur (thigh bone) and tibia (shin bone). He then maps the anatomy of your knee joint with a specialised probe. This information, together with data from the navigation pins, is detected by a specialised camera. This is then entered into the Mako robotic unit. This allows adjustments to the surgical plan based on additional detailed information obtained during surgery. The Mako system then guides Dr Limbers within the pre-defined area while he prepares the bone for the implant (Figures 3&4). The tactile, auditory and visual feedback of the robotic arm limits the bone preparation to the diseased areas and allows real time adjustments. This technique provides highly accurate placement and alignment of the components of the partial knee replacement. After the bone preparation Dr Limbers implants the metal femoral and tibial components with a polyethylene insert between the components.
At the end of the surgery, local anaesthetic is injected into the wound for pain relief. The wound is then carefully closed and covered with a waterproof dressing. Typically, you will remain in hospital for 1 night then be discharged the next day after seeing the physiotherapist. Your physiotherapist will set goals with you to get you back on the move. You will have outpatient physiotherapy after discharge. Your physiotherapist will closely monitor your condition and progress. Dr Limbers will review you with an X-ray of your new partial knee replacement in his rooms after 6 weeks.
Most of the recovery will be obtained in the 1st 6 weeks, with further recovery continuing for several months beyond that. The post-operative pain is less and the recovery quicker than with a full total knee replacement.
Medium term data of robotic partial knee replacement suggests a significantly lower incidence of premature failure, when compared to traditional instrumented partial knee replacement techniques. It results in a more rapid recovery and shorter hospital stay than traditional total knee replacement surgery, as well as a more natural feeling knee following surgery.
For Patients
Conditions
Procedures

I'm 6weeks post operation of a total knee replacement, walking 5km at a normal pace. Minimal to no pain after just a couple of weeks
I believe this is due in most to John's skills and his choice of proceed & components.
If you are in the need of an Orthopaedic surgeon, you could do no better than to talk to John about what you may require. His advice is delivered in a straight forward, well explained manger which provides the confidence that you want to under go this procedure.
I find it hard to believe how much I have improved so much, so quickly and almost zero pain. I am walking without aids and I haven't felt this good in years. His staff and all those at Gosford Private Hospital were also amazing with their care and support, prior to operation, during hospital and Exercise Physiologists Post Op rehabilitation. I cannot thank him enough, I only wish I had done it sooner. If you want Terrific care from a Professional, Caring and Dedicated Team then call Dr.John Limbers now !!!
In March 2025 I needed a full knee replacement and once again I was fortunate to have my surgery done by Dr.John Limbers and his team at Gosford Private Hospital.
As previousley stated, the care, professionalism and support from Dr. Limbers and his whole team was amazing. I knew in advance what to expect in terms of pain and post operative management. They were so incredibly thorough and supportive
Pre op, during hospitalisation and Post operative treatment.
I cannot thank Dr.John Limbers and his team enough and would not hesitate to recommend them to anyone who is experiencing
joint and mobility issues. If you are suffering then call Dr Limbers
immediately and make an appointment, you will be so glad you did !!!
From
; Chris Kokegei an eternally grateful patient.
As in my earlier review below, I feel an enormous debt of gratitude to John Limbers for his technical skill and an outcome beyond my expectations. On top of this, his daily contact and reassurance along with meaningful follow up after discharge make him someone I would recommend without any reservations at all.
Since I had experienced periods of strong RH knee pain starting 8 years ago, which had steadily increased in discomfort until 7 weeks ago, I finally had a full knee replacement performed by the incredible Dr John Limbers and his team at the SAN hospital at the end of February.
I was home 6 days later, able to use the stairs with just the rail for assistance (3 storey home) and not needing crutches from day one. It has been a day by day improvement in mobility since then. Surgical discomfort from exercising has only required a reducing Panadol intake for the last 3-4 weeks.
Without any doubt John Limber's huge experience, skill level with the Mako procedure and ability to communicate and reassure, have given an outcome which is completely satisfying to both me and my family.
As well, on top of his obvious surgical skills he is both a gentleman and a caring individual.
Thank you Dr. Limbers!
Dr Limbers replaced both my knees on 30/1/25.
6 months later I have zero pain and exceptional mobility and flexibility in both knees.
Dr Limbers, I couldn’t be happier or more grateful…. Thank you 🙏🏻
Anyone considering knee replacement surgery, I highly recommend Dr Limbers.
His staff are also super nice and extremely helpful, even organising my health fund rebate post surgery for me.
They’re a fabulous team. 🙏🏻🙏🏻
I am deeply honoured to provide this long-overdue reference for my great friend and exceptional orthopedic surgeon, Dr. John Limbers.
In my experience,
Dr. Limbers is one of the country's most dedicated, caring, and skilled professional orthopedic surgeons.
His Exceptional Skills and Knowledge are unmatched.
As a patient, I have witnessed Dr. Limbers' exceptional skills firsthand. His lectures to a broad audience of professionals, including my esteemed friends and Laureate Medical Professors,
John has consistently demonstrated his love, knowledge, and abilities far beyond exemplary.
Unwavering Commitment👈
Dr. Limbers' dedication to his craft is inspiring. His commitment to delivering outstanding results is evident in every aspect of his work. His skills and knowledge have significantly impacted my life, particularly regarding my knee and wrist surgeries.
100% Functionality Regained
Thanks to Dr. Limbers' love, dedication, and expertise, I have regained 100% functionality in my knee and wrist. His professionalism, care, and attention to detail are truly exceptional.
A Legend in His Field
Dr. John Limbers is a legend in his field, and I am not alone in my admiration for his work. His contributions to orthopedic surgery are invaluable, and I am grateful for the opportunity to work with him.
Conclusion
If I were to win ten million dollars today, I would still be back at work tomorrow. However, I would be eternally grateful for the exceptional care and expertise that Dr. Limbers has provided. Thank you, Dr. Limbers, for being an outstanding surgeon, educator, and professional.
Warm regards,
Gerrit Duits
Baumeister Pty Ltd
Thanks to you and your staff Dr Limbers
I can recommend Dr Limbers and his staff to anyone needing hip replacement surgery to provide the best possible outcome.
I cannot recommend him enough,if you’re looking for hip or knee replacement go to the best in my opinion.
Thank you Dr Limbers
Dr Limbers is a very caring Surgeon and has done a fantastic job with my knees. I am now walking straight and i am no longer bow
legged. If you are wanting a new quality of life don't put it off.
Thanks Dr John.
Gave me a double knee replacement, told me of all the risks ECT, and how long it would take me to heel.
I sincerely want to thank Dr John Limbers for giving me my life back.
Thanks for your amazing care and support
From the Mead Family.
I can only praise Dr. Limbers for his expertise with the operation and wholeheartedly recommend his skills to anyone with hesitation about going ahead with this surgery.
However, I must mention here that my own perseverance following the recommendations from the physiotherapists helped with my recovery which after 6 weeks was excellent.
Extremely happy with the outcomes in both cases.
Dr Limbers is very caring surgeon.
I have no hesitation in recommending Dr Limbers to others, if I could give 6 stars I would!
Brilliant result with excellent pain management.
If you think you need a TKR, do it now and don’t put it off. The sooner you get it done, the sooner you get back to your old life again.
Thank you Dr Limbers!!!
I cannot speak highly enough of Dr Limbers’ extraordinary skill, patience, consideration and kindness.
I have my life back pain free
You are amazing and your team eternally greatful
Thanks Steve Field
Since 3 years ago, Dr Limbers is much the same fellow per my comments below, maybe now even better. He has also improved his methodology with even more analysis of the lumbar and pelvic positioning w.r.t. the TRH to be done. Pretty impressive.
With the 2nd THR, so other side and am now bilateral, I was far more prepared physically and mentally; I'd strongly urge anyone getting THR to get a PRE-op plan from a physio, then about 2-3 weeks after surgery, do a POST-op plan with them. I did this time around, not the 1st, and the outcome after is even better. Per discussion with Dr L, I am about 6-7 wks ahead of 1st operation; back full time at gym 12 days after surgery, referring first grade u14 soccer (e.g. running) and have already booked winter ski trip with kids.
So all up, really successful two ops. If you have any concerns or any sort of questions do not be shy about asking Dr Limbers, he will carefully and wisely recommend options that are in your best interest.
Also should be noted his staff in Sydney office are very good; polite and prompt to answer any questions or concerns.
====
Dr Limbers did my TRH in Jan 2020.
I would 110% concur with all the 5/5 previous reviews; Dr John is not only a great surgeon but his 'bed side manner' at the referral, in surgery, immediate post-op check, and 6 week follow-up where exceptional. Don't get me wrong, you should choose a surgeon on skill and results but the non-tangible comes into it too. In my case, I am very technically oriented and cross check everything at work and home. No different here; I consulted three surgeons and although they were all good, Dr John out scored them not only technically but also on the human side so that I felt comfortable to ask technical and medical questions more than adequately. He listened carefully to not only my questions but also my suggestions for certain types of prosthetics that he happily gave me pros and cons for.
Another thing to consider - although Dr John is good he knows he can do better ... by using a robot (Mako) as part of the surgery; it assists in getting the position as correct as possible. He will explain better than I, but it is a no brainer that a technical or medical person should use the best tools available to them. If they can get better accuracy and a better result, costs considered, then why not use it? This was one of my main criteria was to find a surgeon that used a Mako robot to assist and get the 'replacement parts' put into the right angle, distance and length. I wanted as close as possible a natural result as I am young and do a lot of sports with my kids - Dr Johns achieved that in spades. I am very pleased.
Dr Limbers was once responsible for very successfully repairing my severed achilles tendon and now has done a superb job of giving me a new knee that will allow me to return to my sporting activities. He is an excellent surgeon , very thorough and most informative. I cannot thank him enough.
and empathetic person. We can now venture onto our 3 month overseas trip in June Thank you Dr John!!
After having pain for many years and poor mobility I now live a pain free life and can walk long distances and exercise with great ease.
I am very thankful to Dr Limbers for turning my life around. 😊
Replacement surgery cancelled it March due to COVID 19
I had my surgery Rescheduled On 2nd July
I,m now home feeling so happy with everything
Dr limbers is a professional,I would not hesitate in using him again if needed
I,m up walking , I can actually stand up straight without kicking out my butt
The pain I had for last 2 years has completely gone , I,m so happy
With everything , I can’t wait untill I heal so I can get my life back
Just to walk without thinking about it is amazing , thankyou dr limbers and team ,having both hips done at same time is so worth it ..
Best regards
Tracey peterson
Post-surgery whilst in hospital he checked in regular on my progress. Along with the great post and rehab team I am back on the bike and have great flexion and returning strength.
I at some point will need my other knee done and I would not hesitate in going back to Dr Limbers.
Thank you for helping me return to a normal life.
Regard
Michael Hull
Dr Limbers has such good communication skills, I was given a detailed explanation of what was going to happen pre & post operation.
The Robotic surgery left minimal scarring & physiotherapy has improved my flexibility.
It gets better each day thanks to the techniques used.
Thanks John, I look forward to a pain free journey ahead.
The range of motion and relaxed muscles after only 8 weeks surprised my chiro. Even the leg length was the same for both legs. For years my pelvis was rotating as the left hip muscles tightened and the left leg shortened as a result of the pelvis rotation between chiro visits and this time pelvis hadn't rotated.
I am lucky that my GP referred me to Dr Limbers and strongly recommend Dr Limbers to anyone considering a hip replacement.
Financially Dr Limbers is very reasonable, and apart from his surgical skills , his bedside manner is very caring. Whilst I was in hospital he visited me and his other patients every day. I would highly recommend Dr Limbers. I would like to mention Dr Limbers surgical assistant Sr Leanne Flynn. I received a phone call from this lovely lady a few days after my surgery once I was discharged from hospital. Sr Leanne was concerned how my recovery was going and was very helpful with advice. Thank you very much Dr Limbers and your team.
Addition, one year later (September 2022): He did my other knee - same great result… that knee also doing very well no indeed. Can’t recommend Dr Limbers enough.
I would strongly recommend treatment by Dr Limbers for anyone seeking a knee replacemen.
I had put up with it for years I could only walk for five minutes then pain would kick in,Since having my knee replaced nine months ago I now have a great Quality of life back I’m 70years of age I am now walking ,working around the house ,all so woking casual as a bricklayers labourer , plus I’m back to playing Baseball and running bases freely, I have recommended DrLimbers to two of my friends who will now go to see him,
I thoroughly recommend Doctor John Limbers.
I would like to recommend him as he gives first class services and follow up.
Listens to the patient
Explains things so patient understands what the procedure & how it is done
Takes his time does not rush you out the door
Will assess patient regardless of his old age
After care is explained & reassured that any problems or questions just ring
No out of pocket fees
All round very pleasant experience
Dad had a a Rt mako robotic anterior total hip replacement at age 89
Up & walking days later pain free 1 wk later
Would highly recommend Dr limbers
As with my knee post op, Dr Limbers was again actively interested in my recovery; not that there was much to do. I can only guess that the quick recovery is due to him being extraordinarily careful during the surgery.
The anesthetist working with Dr Limbers on both of my surgeries was Dr Coonan. Again, no problems at all and he was very careful in discussing my medical history before deciding what to do during the surgery. A really nice bloke as well.
From my experience I thoroughly endorse and recommend Dr Limbers, Dr Coonan, the San Hospital and their wonderful staff and I also recommend robotic surgery for hips and knees.
If you read this good luck with your surgery!!
I was pain free and walking without any aids within three weeks.
I felt very confident prior to the operation as Dr Limbers explained in detail how he would perform the surgery.
His admin staff are very pleasant and helpful to deal with.
I would highly recommend Dr Limbers and his team.
Update. Runner up in golf club championship this year 4 mths later walking. Yes that hip is fixed...
Dr John Limbers performed bilateral hip replacement surgery and the operation has truly changed my life.
I was out of hospital in 5 days, underwent rehabilitation at home and now 6 weeks later I have resumed all the above activities with minimal discomfort and continue to improve week by week.
His expertise and kindness has changed my life.
I will be forever thankful.
My ankle has improved immeasurably. I can now walk with a straight leg. My hip pain has gone and my knee pain has reduced considerably. I am cross training, playing walking football and bush walking. I have more mobility and strength in my ankle than I have had in 15 years. My quality of life has increased and I hope to start running again in the new year.
Dr Limbers has a caring manner which I have not always found with specialist surgeons. I am very pleased to have chosen Dr Limbers for my surgery.
Thanks Doc
ll Kind Regards Chris
Dr Limbers is very professional and friendly and explained my hip replacement in full detail. I was booked for surgery within 4 weeks.
The care and attention I received from my first appointment to the 6 week follow up was excellent. The procedure and all the staff at Gosford Private were amazing Doctors, Nurses Physio and the lovely catering staff could not be more caring and attentive. The food was plentiful and extremely enjoyable. Facilities were very clean and well looked after.
Dr Limbers office staff were very pleasant and helpful at all times.
I would recommend Dr Limbers to anyone looking for an orthopaedic surgeon he is a very special specialist!
I was told I needed a second TKR. The SAN introduced me to Dr.John Limbers and he recommended the MACRO ROBOTIC TKR. Allelujia!! what a difference 12 years can make. Different Surgeon and different Method. Consequently, a quicker recovery and faster mobility.
Thanks so much to the professional skills endowed to Dr. J. Limbers and his friendly and jovial manner. Will certainly recommend him to my dear and suffering friends. Anita Curtis
Finally, in desperation, I asked my very helpful GP Dr Howard Oxley to refer me to the best Orthopedic Surgeon he knew in my area ! My GP did a great and wonderful service in referring me to Dr John Limbers !
My experience right from my first interview with Dr John Limbers, last interview and all surgical procedures in hospital was 'first class'.
Initially, Dr Limbers demonstrated the Mako Robotic knee surgery procedure, and asked me if I would like to take part in the 360 Patient Partner Program he has introduced for patients pre and post surgery physiotherapy needs.
A wonderful 360 Patient Partner Program physiotherapist Denise Korhonen took me through the 8 week program via virtual video daily exercises and bi-weekly interviews with great care, professional advice. and kind attention. The program also supplied a free Garmin watch, and an inflatable knee unit for applying ice packs post surgery.
I can highly recommend the 360 Patient Partner Program Dr Limbers advises to patients, as well as sincere gratitude to the nurses and physiotherapists of Gosford Private Hospital who looked after me so kindly and professionally.
The result ? At 78, after 6 weeks, I am now walking 'Prince' my precious Welsh Corgi over 4,000 steps a day, including gardening, and daily duties all without pain, and without a stick !!
Thank you Dr John Limbers, Denise Korhonen, and GP Dr Howard Oxley from a very satisfied patient.
Harold Gibbs JP
Dr Limbers is not only a superior surgeon but he is also conscientious, visiting every day while I was in hospital. I now have two perfect hips that will last me the rest of my life. Highly recommended!
I was initially advised by someone else that I would not require surgery after reviewing my MRI and would be fine after a few weeks, 8 weeks had past with no change to the pain in my leg and knee area. Thankfully a visit to Dr Limbers saved me the agony or continuing with the injury, two weeks later the surgery was carried out and I am a new man ! 👏🏼👏🏼👏🏼 Thank you Sir !
required or assistance). I can’t speak highly enough of Dr
Limbers & his knee replacement procedure. I found him to be a very caring man, & his staff happy & caring which helped me feel more relaxed and supported through a rather anxious time.
I have no hesitation whatever in recommending Dr Limbers, whom I found to be highly professional, courteous and very likeable.
If you are living with knee pain and restricted movement related to the deterioration of the knee joint, I was. I was in considerable pain and it was affecting my movement and quality of life even driving and sleeping. I was referred to Dr Limbers and before attending I did my research
I found Dr Limbers to have a professional and caring nature. From my very first consultation, to his daily visits while I was in hospital and then my follow up consultation. I felt my needs were valued and supported with every question I put to him answered in detail.
I must also add that my anaesthetist, Dr Gray certainly put my mind at ease giving me a bit of a pep talk when I informed him of my ‘possible unrealistic’ fear of the anaesthetic process. The reception girls were wonderful and very friendly and the staff at Gosford Private, in the ward and in rehab were exceptional in their care and professionalism.
All round Dr Limbers and his team made my journey as professional and comfortable as possible and I would highly recommend them for orthopaedic surgery.
My hip replacement in November was a breeze, back at home in 3 days, an outstanding recovery. I would recommend John Limbers to anyone who wants to have the best surgical experience.